500 Ohm Resistor Color Code, Features - Can 510 Ohm Resistor be used instead?
500 Ohm Resistor Color Code, Features - Can 510 Ohm Resistor be used instead?
A resistor is a fundamental electronic component used to control the flow of electrical current. A 500 ohm resistor is a resistor that has an impedance of 500 ohms.
The following are the characteristics, uses, and application fields of 500 ohm resistors.
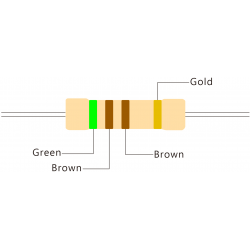
For 4-ring 500 ohm resistors with a tolerance of ±5% (gold),
the color codes are:
Green (5) Black (0) Brown (1) Gold (±5%)
500 Ohm Resistor Characteristics:
Impedance: The basic characteristic of a resistor is its impedance. In this case, the resistance of the resistor is 500 ohms. This means that with a voltage of 1 volt,
the current through the resistor will be 0.002 amps (or 2 milliamperes).
Linear: An ideal resistor is linear, meaning its impedance relates to voltage and current according to Ohm's law.
Energy Dissipation: Resistors convert electrical energy into heat, which is an important characteristic of them.
No frequency dependence: With the exception of some special resistors (for example, inductive or capacitive resistors),
the impedance of most resistors (including 500 ohm resistors) is independent of frequency.
500 Ohm Resistor Use:
Current Control: Resistors are important components in electronic circuits for controlling current. A 500 ohm resistor can be used to limit the current.
Voltage Dividing: Resistors can be used to make voltage dividers, which are simple circuits used to step down voltage.
Filtering and Coupling: In RC (resistor-capacitor) circuits, resistors are used for filtering and coupling.
Tuning Circuits: In amplifiers and radio frequency circuits, resistors are used to adjust and tune the performance of the circuit.
500 ohm resistor price factor:
The price of a 500 ohm resistor depends on several factors including resistor type (through-hole or surface mount), power rating, tolerance, package quantity, and supplier.
Material cost: The material of the resistor will affect its price. High-quality, high-resistance, or special-purpose materials often drive up the price.

Manufacturing Cost: This includes the cost of labor, energy and equipment involved in the manufacturing process of the resistor.
Specifications and Accuracy: The specification and accuracy of a resistor also affects its price.
Higher precision resistors require tighter quality control during manufacturing, which can increase manufacturing costs.
Brand: Sometimes, brand is also a factor that affects price. Well-known manufacturers of electronic components may charge higher prices for their products,
in part because of their brand power.
Buying in bulk: The quantity you buy can also affect the price. Usually, resistors will cost less when purchased in bulk than individually.
Supply and Demand: Market supply and demand also affect the price of resistors. If there is sufficient supply, the price may decrease; conversely,
if demand exceeds supply, the price may increase.
Shipping cost: The cost of shipping the resistor to the buyer will also affect the final selling price of the resistor. This includes shipping,
customs duties and other associated logistics charges.
Technical characteristics: For example, some resistors may have special resistance to heat or cold, or have properties such as water and dust resistance,
which may affect their price.
All of the above factors may affect the price of the 500 ohm resistor, and the specific price needs to be determined according to the actual situation.
Application fields of ohmic resistance:
Electronic equipment: Resistors are widely used in various electronic equipment and circuits, including computers, mobile phones, TVs, etc.
Industrial Control Systems: In industrial control systems, resistors are used to control the current flow to motors, pumps, and other equipment.
Power Systems: In power systems, resistors can be used to control and balance current flow.
Measurement and Test Equipment: In measurement and test equipment, resistors are used to create precise voltages and currents.
Audio Equipment: In audio equipment, resistors are used to control volume and tone.
These are just some basic applications and characteristics of 500 ohm resistors, their actual use can be more complicated and specialized,
depending on specific application requirements and circuit design.

Replace the 500 ohm resistor with 510 ohm resistor:
Method 1: 500 ohm resistor color codes are not available because 500 ohm resistors are non-standard resistor values:
The 500 ohm resistor color code is substituted with 510 ohm because the closest standard value (500 ohm resistor) using a 510 ohm resistor is 510 ohm.
The final practical value of the 510Ω resistor is between 487.5Ω-532.5Ω
The percentage error is only 2%, so you can replace the 500 ohm resistor with a 510 ohm resistor and the circuit performance remains almost the same.
Solution 2: It is to connect two 1000 ohm resistors in parallel, that is, 1 kΩ || 1kΩ = 500Ω
500 ohm equivalent resistance
You have to make sure that when using any type of combination the resistors used should be precision resistors or can have a 5% tolerance level.
With the above two methods, you can replace the 500 ohm resistor for your circuit.
510 Ohm Resistor Color Code:
(Green, Brown, Brown, Gold)
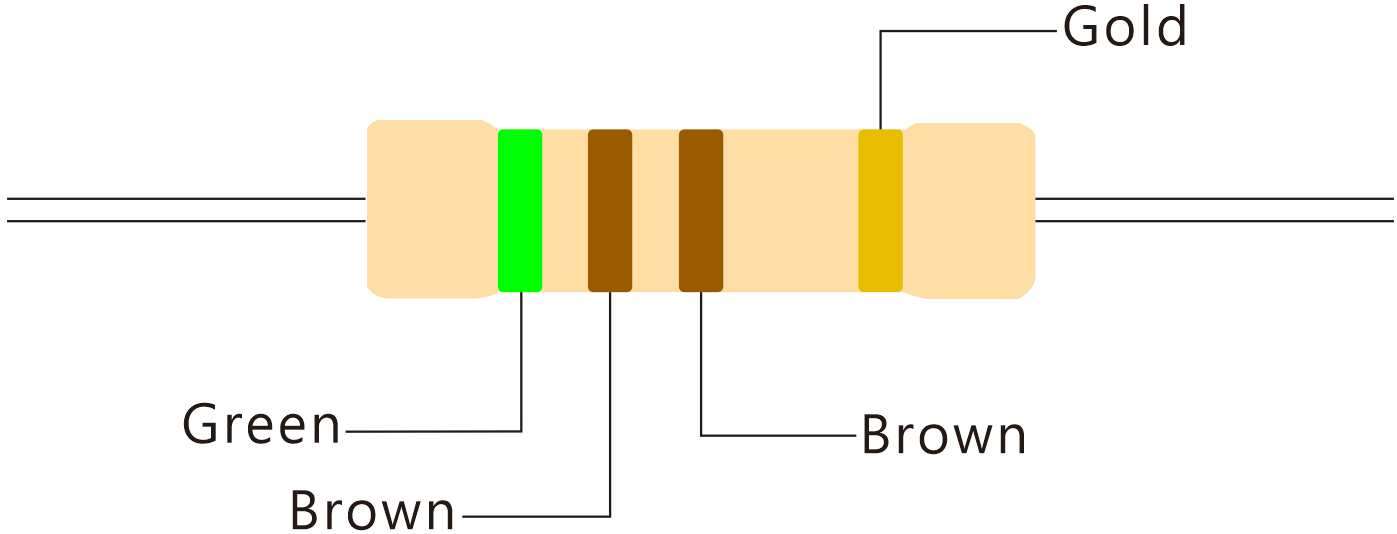
1st digit 5
2nd digit 1
3rd multiplier 10 510 Ohms
tolerance
+- 5%
Below are instructions for using resistor color codes for 4-ring resistors
The color of the first band indicates the value of the first significant figure. The first band is green and corresponds to a value of 5.
The color of the second band indicates the value of the second significant figure. The band is blue and corresponds to a value of 6.
It is added to the right of the first number (starting with 1). Therefore, the number for the first band and the second band is: 56.
The third color band represents the decimal multiplier, and the first two digits must be multiplied together to obtain the resistance value of the resistor.
Take the numbers and multiply them by the value given by the band. The actual multiplier is 10 n, where n is the value of the color of the stripe.
In this example, the third band is blue and corresponds to the number 6. So the multiplier is 10 6 = 1000000.
So the color gives a total resistance of 56 x 10 6 Ω = 56000000 Ω.
The fourth ring represents the tolerance value. In this example a gold band is used with a tolerance of 5%.
As a result, the resistance value of the green, blue, blue and gold ring is 56M ohms, with a tolerance of ±5%.
The following is the formula for calculating the resistance color scale
The calculation formula is:
first band = green = 5 (first number)
2nd strip = brown = 1 (2nd number)
3rd band = brown = 10 (multiplier)
4th ring = gold = ±5% (tolerance)
Therefore, 51 ×10±5% ==> 510 Ω ==> 0.51 k Ω
Tolerance is considered ==> 5%of510 ==> 22.5 Ω
It will help you identify the color code of the resistor accurately and quickly.







