Previous Chapter:PT2313 IC Datasheet, Equivalent, Circuit Diagram, and Voltage
Next Chapter:What is a power module
What is memory and why is it important?

Post Date:2024-04-26,HY
What is memory and why is it important?
The memory unit is actually a kind of sequential logic circuit. According to the type of use of memory can be divided into read-only memory (ROM) and random access memory (RAM), the function of the two has a large difference, so the description is also differentA memory is a collection of many storage units, arranged in unit number order. Each unit consists of a number of binary bits to represent the value stored in the storage unit, this structure is very similar to the structure of the array, so in the VHDL language, usually by the array to describe the memory
The units of storage capacity of memory mainly include bytes, kilobytes, megabytes, gigabytes, terabytes, and other larger units.
Among them, Byte is the basic unit used to measure storage capacity in computer information technology, and a byte is equal to 8 bits. The commonly used rate is 1024, that is, 1KB is equal to 1024 bytes, 1MB is equal to 1024KB, 1GB is equal to 1024MB, and 1TB is equal to 1024GB.

Memory function
Memory is a memory component used to store programs and various data information. Memory can be divided into main memory (referred to as main memory or memory) and auxiliary memory (referred to as auxiliary memory or external memory) two categories. It is main memory that exchanges information directly with the CPU.The working mode of main memory is to store or read all kinds of information according to the address of the storage unit, collectively referred to as access memory. The carrier that collects the storage units in the main memory is called the storage body. Each unit in the storage body can store a string of information represented by binary code. The total number of bits of information is called the word length of a storage unit. The address of the storage unit corresponds to the information stored in it. The address of the storage unit is only one, which is fixed, and the information stored in it can be replaced.
The binary code indicating each unit is called an address code. When you look for a unit, you first give its address code. The register that stores this address code is called the memory address register (MAR). A memory data register (MDR) is also set up to store information taken from a storage unit of main memory or to be stored in a storage unit.
Classification of memory
Memory can be divided into random access memory (RAM), read-only memory (ROM) and Cache. Random access memory: The contents of any storage unit can be accessed randomly, and the access time is independent of the physical location of the storage unit. Read-only memory (ROM) : The content of the storage is fixed, can only be read out but not written to the semiconductor memory, etc.
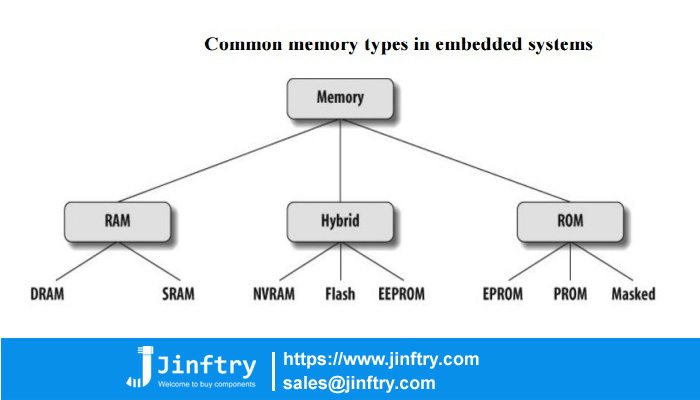
Semiconductor memory: Memory composed of semiconductor devices.
Magnetic surface memory: memory made of magnetic materials.
2. Sorted by storage mode
Random access memory: The contents of any storage unit can be accessed randomly, and the access time is independent of the physical location of the storage unit.
Sequential memory: It can only be accessed in a certain order, and the access time is related to the physical location of the storage unit.
3. Classified by memory read and write function
Read-only memory (ROM) : Semiconductor memory in which the contents of the storage are fixed and can only be read out but not written.
Random read/write memory (RAM) : semiconductor memory that can be both read and written.
4. Classified by information retention
Nonpermanent memory: memory in which information disappears after power failure.
Permanent memory: memory that can retain information after power failure.
5. Classified by function in computer system
Main memory (memory) : used to store active programs and data, with high speed, low capacity, and high price per unit.
Auxiliary memory (external memory) : mainly used to store currently inactive programs and data, its slow speed, large capacity, low price per unit.
Buffer memory: mainly in two different working speed components play a buffer role.
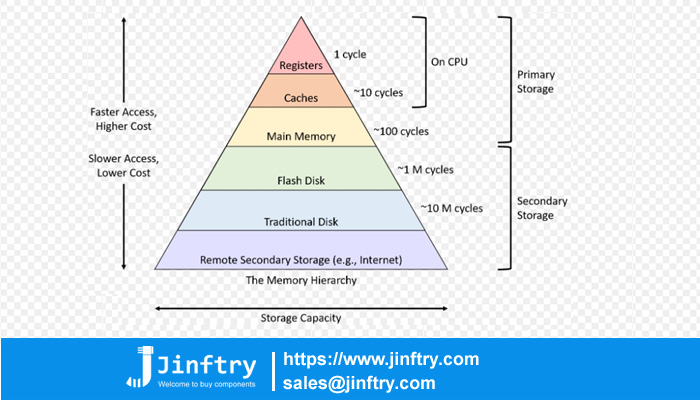
Hierarchy of memory
Registers (Registers). Located at the top of the memory hierarchy, it is the fastest memory inside the CPU for storing temporary data and instructions, with fast access and small capacity.
Cache (Cache). Located between the CPU and the main memory, it is composed of multiple layers, such as L1, L2, L3 cache, which is used to store the recently accessed data and instructions to reduce the latency of accessing the main memory, and its access speed is faster and the capacity is smaller.
Main Memory (Main Memory). Also known as memory, is the main storage medium in the computer system, usually composed of DRAM (dynamic random access memory), the capacity is large, the distance between it and the CPU is far, so the access speed is relatively slow.
(Secondary Storage). Used for long-term storage of data and programs, such as hard drives, optical disks, and solid-state drives (SSDS), which have larger capacities than main memory but slower access speeds.
In MCS-51 series microcontroller, the program memory and data memory are independent of each other, and the physical structure is not the same. Program memory is read-only memory and data memory is random access memory. From the physical address space, there are four storage address Spaces, namely, on-chip program memory, off-chip program memory, on-chip data memory and off-chip data memory, and the I/O interface is uniformly addressed with the external data memory
Previous Chapter:PT2313 IC Datasheet, Equivalent, Circuit Diagram, and Voltage
Next Chapter:What is a power module




