MKP1839439124HQG vs BFC241814704
| Part Number |
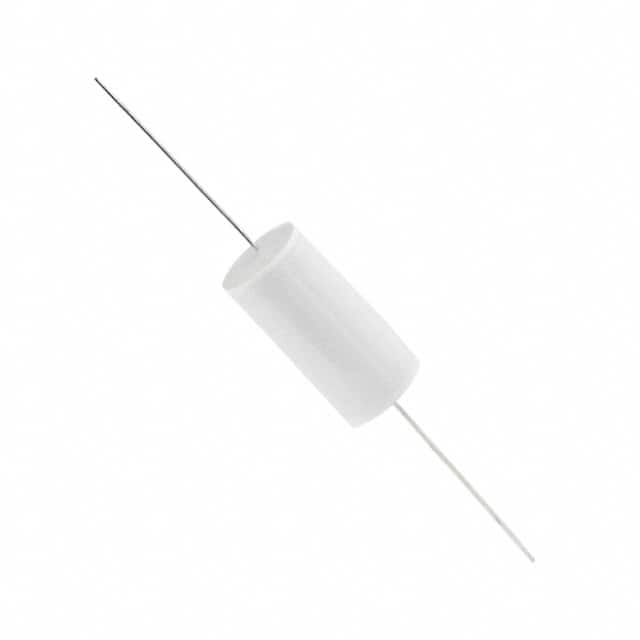

|
|
| Category | Film Capacitors | Film Capacitors |
| Manufacturer | Vishay Beyschlag/Draloric/BC Components | Vishay Beyschlag/Draloric/BC Components |
| Description | CAP FILM 0.39UF 5% 1.25KVDC AXL | CAP FILM 0.47UF 2% 250VDC RADIAL |
| Package | Tape & Box (TB) | Tape & Reel (TR) |
| Series | MKP1839 HQ | MKP418 |
| Features | - | - |
| Operating Temperature | -55°C ~ 110°C | -55°C ~ 85°C |
| Mounting Type | Through Hole | Through Hole |
| Package / Case | Axial | Radial |
| Applications | High Pulse, DV/DT | High Frequency, Switching |
| Tolerance | ±5% | ±2% |
| Size / Dimension | 0.591" Dia x 1.240" L (15.00mm x 31.50mm) | 0.689" L x 0.335" W (17.50mm x 8.50mm) |
| Termination | PC Pins | PC Pins |
| Voltage Rating - AC | 425V | 25V |
| Voltage Rating - DC | 1250V (1.25kV) | 250V |
| Lead Spacing | - | 0.591\" (15.00mm) |
| Ratings | - | - |
| Height - Seated (Max) | - | 0.591\" (15.00mm) |
| Capacitance | 0.39 µF | 0.47 µF |
| ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) | - | - |
| Dielectric Material | Polypropylene (PP), Metallized | Polypropylene (PP), Metallized |

-
1. What are the uses of film capacitors?
High-frequency filtering, power decoupling, power noise bypass
The main uses of film capacitors include high-frequency filtering, power decoupling, power noise bypass, etc. In electronic devices, film capacitors are widely used in various circuits due to their high insulation impedance, wide frequency response and self-healing properties.
Specific application scenarios
High-frequency filtering: Film capacitors have excellent high-frequency insulation performance, and the capacitance and loss angle are independent of frequency in a large frequency range and change little with temperature, so they are often used in high-frequency filtering circuits.
Power decoupling: In car audio systems, film capacitors are used for power decoupling to ensure stable power supply and avoid noise caused by feedback generated by the power supply.
Power noise bypass: Film capacitors are also widely used for power noise bypass (reverse cross-connection) to reduce the impact of power noise on the circuit.
Different types of applications
CBB film capacitors: widely used in circuit boards because of their high insulation impedance and wide frequency response.
Organic film capacitors: Made of materials such as polypropylene film and polyester film, they have excellent performance, a wide variety of varieties, and a wide range of applications. They are suitable for a variety of electronic devices.
-
2. Can film capacitors be used for AC?
Yes
Film capacitors can be used for AC. Film capacitors can work normally in AC circuits and have specific application scenarios and advantages.
Structure and working principle of film capacitors
Film capacitors are mainly composed of metal foil (or foil obtained by metallizing plastic) as electrode plates and plastic film as dielectric. Common plastic films include polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene or polycarbonate. These capacitors are usually made by winding or stacking processes to form a cylindrical structure. -
3. How do film capacitors fail?
High working environment temperature, improper selection of working current, exceeding the specified working voltage, harmonic current
The main reasons for film capacitor failure include the following:
High working environment temperature: Film capacitors can work normally in a temperature environment of -40℃~+105℃, but exceeding this range will accelerate thermal aging, resulting in a shortened service life, and even bursting in severe cases.
Improper selection of working current: The current value in the circuit should be less than the current value allowed by the film capacitor, otherwise it will cause the capacitor to heat up, and long-term use will shorten the life, and even burst in severe cases.
Exceeding the specified working voltage: Excessive voltage will cause partial discharge, which will then break down the capacitor and cannot be used.
There are harmonic currents: high-order harmonic currents are superimposed on fundamental currents, resulting in an increase in total current, causing capacitor load overload, internal expansion, and explosion.
Buying inferior capacitors: In order to reduce costs, some manufacturers on the market use low-quality materials to produce capacitors, which greatly reduces the actual withstand voltage and life of such capacitors.
The structural characteristics of film capacitors and the impact of the use environment on their performance:
Film capacitors are usually composed of polypropylene film, aluminum foil and plastic shell. Polypropylene film is sensitive to high temperature, which accelerates its aging and shortens the life of the capacitor. In addition, a humid environment will also cause water vapor to enter the capacitor, affecting its performance.
-
4. What is the difference between foil capacitors and film capacitors?
Electrode materials, structure, and application areas
The main difference between foil capacitors and film capacitors lies in electrode materials, structures, and application areas.
Electrode materials and structures
Foil capacitors: Foil capacitors usually use metal foil as electrodes. This electrode is formed on a plastic film by vacuum evaporation, which is called a metallized film. This structure can save the thickness of the electrode foil, thereby reducing the volume of the capacitor and making it more miniaturized.
Film capacitors: Film capacitors use plastic films as dielectrics. Common plastic films include polyethylene, polypropylene, polystyrene or polycarbonate. These films overlap at both ends and are rolled into a cylinder to form a capacitor.

