T491A335K006AT vs T540D157K006CH8505
| Part Number |

|
|
| Category | Tantalum Capacitors | Tantalum - Polymer Capacitors |
| Manufacturer | KEMET | KEMET |
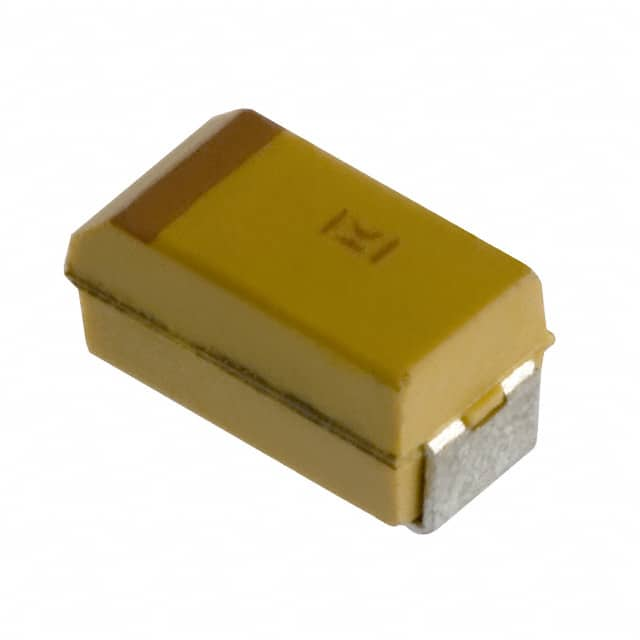
| Description | CAP TANT 3.3UF 10% 6.3V 1206 | CAP TANT POLY 150UF 6.3V 2917 |
| Package | Tape & Reel (TR) | Tape & Reel (TR) |
| Series | T491 | KO-CAP® T540 |
| Type | Molded | Molded |
| Features | General Purpose | High Reliability |
| Operating Temperature | -55°C ~ 125°C | -55°C ~ 125°C |
| Mounting Type | Surface Mount | Surface Mount |
| Package / Case | 1206 (3216 Metric) | 2917 (7343 Metric) |
| Tolerance | ±10% | ±10% |
| Size / Dimension | 0.126" L x 0.063" W (3.20mm x 1.60mm) | 0.287" L x 0.169" W (7.30mm x 4.30mm) |
| Voltage - Rated | 6.3 V | 6.3 V |
| Lead Spacing | - | - |
| Ratings | - | COTS |
| Height - Seated (Max) | 0.071\" (1.80mm) | 0.122\" (3.10mm) |
| Capacitance | 3.3 µF | 150 µF |
| ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) | 8Ohm | 40mOhm @ 100kHz |
| Lifetime @ Temp. | 2000 Hrs @ 125°C | 2000 Hrs @ 125°C |
| Failure Rate | - | - |
| Manufacturer Size Code | A | D |

-
1. Why do tantalum capacitors explode?
The main reason is that excessive voltage or current shocks cause internal short circuits, which trigger thermal runaway.
Excessive ambient temperature may also exacerbate this situation. -
2. Will tantalum capacitors deteriorate?
Yes, tantalum capacitors may gradually lose some of their performance when stored for a long time or in adverse environments.
For example, long-term exposure to high temperature and humidity may cause the electrolyte to evaporate or chemically change. -
3. Can I use ceramic capacitors instead of tantalum capacitors?
It depends on the specific situation. If the size, ESR requirements are not high and a specific capacitance value is not required, you can consider replacing it.
But be aware that there are differences in physical properties between the two, and direct replacement may affect the working state of the circuit. -
4. What causes tantalum capacitors to burn out?
Common causes include applying a voltage exceeding the maximum allowable value, excessive current, high ambient temperature, and manufacturing defects.

