T498A475K010ATE2K9 vs T491A106M010AH
| Part Number |
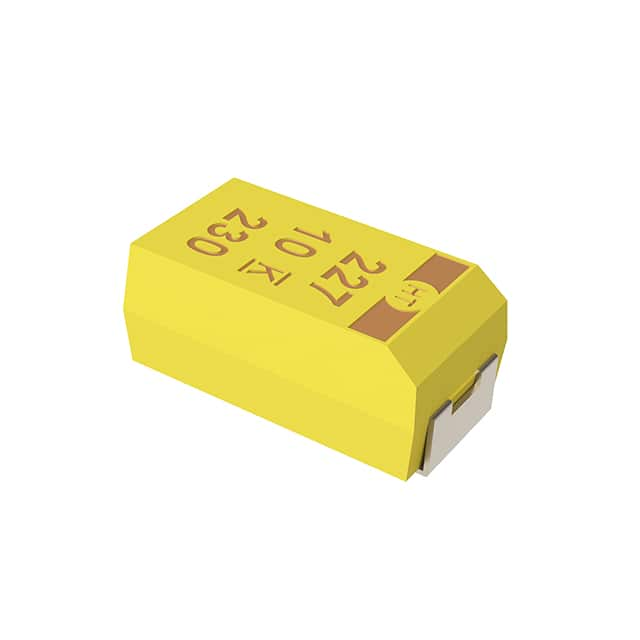

|
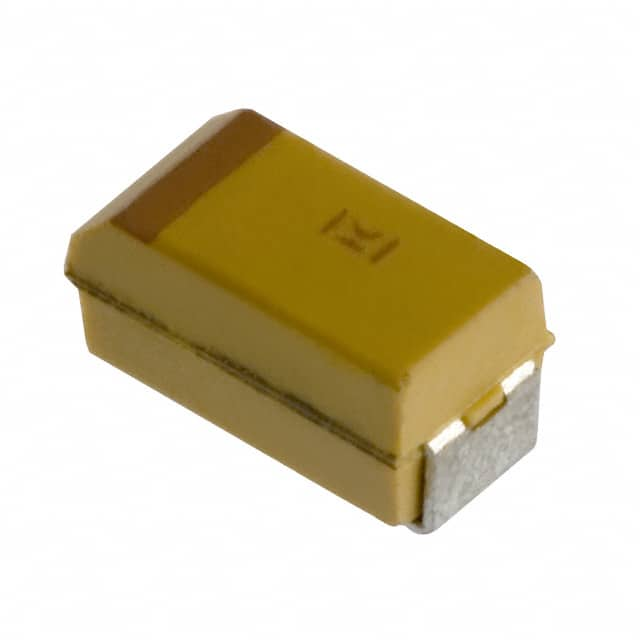

|
| Category | Tantalum Capacitors | Tantalum Capacitors |
| Manufacturer | KEMET | KEMET |
| Description | CAP TANT 4.7UF 10% 10V 1206 | CAP TANT 10UF 20% 10V 1206 |
| Package | Cut Tape (CT) | Tape & Reel (TR) |
| Series | T498 | T491 |
| Type | Molded | Molded |
| Features | Automotive | General Purpose |
| Operating Temperature | -55°C ~ 150°C | -55°C ~ 125°C |
| Mounting Type | Surface Mount | Surface Mount |
| Package / Case | 1206 (3216 Metric) | 1206 (3216 Metric) |
| Tolerance | ±10% | ±20% |
| Size / Dimension | 0.126" L x 0.063" W (3.20mm x 1.60mm) | 0.126" L x 0.063" W (3.20mm x 1.60mm) |
| Voltage - Rated | 10 V | 10 V |
| Lead Spacing | - | - |
| Ratings | AEC-Q200 | - |
| Height - Seated (Max) | 0.063\" (1.60mm) | 0.071\" (1.80mm) |
| Capacitance | 4.7 µF | 10 µF |
| ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) | 2.9Ohm | 4Ohm |
| Lifetime @ Temp. | 2000 Hrs @ 150°C | 2000 Hrs @ 125°C |
| Failure Rate | - | - |
| Manufacturer Size Code | A | A |
-
1. Difference between ordinary capacitors and tantalum capacitors
Material: Ordinary capacitors can be aluminum electrolytic capacitors, ceramic capacitors, etc.; while tantalum capacitors use metal tantalum as anode material.
Performance: Generally, tantalum capacitors have better temperature stability and higher capacity-to-volume ratio.
Application range: Due to its performance characteristics, tantalum capacitors are often used in miniaturized electronic products that require high reliability. -
2. What is the expected life of tantalum capacitors?
Under normal circumstances, it can range from thousands of hours to tens of thousands of hours, depending on the working conditions and manufacturer specifications.
-
3. Why do tantalum capacitors explode?
The main reason is that excessive voltage or current shocks cause internal short circuits, which trigger thermal runaway.
Excessive ambient temperature may also exacerbate this situation. -
4. Will tantalum capacitors deteriorate?
Yes, tantalum capacitors may gradually lose some of their performance when stored for a long time or in adverse environments.
For example, long-term exposure to high temperature and humidity may cause the electrolyte to evaporate or chemically change.

