T540D157K006CH8505 vs T491A155M016AT
| Part Number |
|
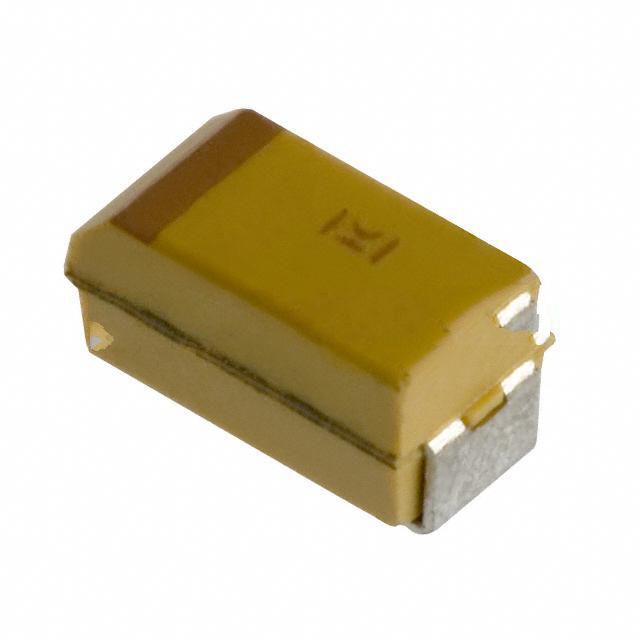

|
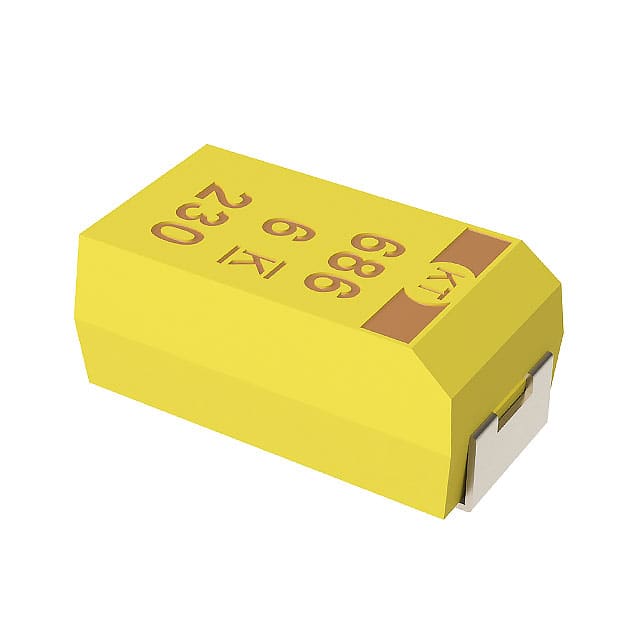
| Category | Tantalum - Polymer Capacitors | Tantalum Capacitors |
| Manufacturer | KEMET | KEMET |
| Description | CAP TANT POLY 150UF 6.3V 2917 | CAP TANT 1.5UF 20% 16V 1206 |
| Package | Tape & Reel (TR) | Tape & Reel (TR) |
| Series | KO-CAP® T540 | T491 |
| Type | Molded | Molded |
| Features | High Reliability | General Purpose |
| Operating Temperature | -55°C ~ 125°C | -55°C ~ 125°C |
| Mounting Type | Surface Mount | Surface Mount |
| Package / Case | 2917 (7343 Metric) | 1206 (3216 Metric) |
| Tolerance | ±10% | ±20% |
| Size / Dimension | 0.287" L x 0.169" W (7.30mm x 4.30mm) | 0.126" L x 0.063" W (3.20mm x 1.60mm) |
| Voltage - Rated | 6.3 V | 16 V |
| Lead Spacing | - | - |
| Ratings | COTS | - |
| Height - Seated (Max) | 0.122\" (3.10mm) | 0.071\" (1.80mm) |
| Capacitance | 150 µF | 1.5 µF |
| ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) | 40mOhm @ 100kHz | 8Ohm |
| Lifetime @ Temp. | 2000 Hrs @ 125°C | 2000 Hrs @ 125°C |
| Manufacturer Size Code | D | A |
| Failure Rate | - | - |

-
1. What are the disadvantages of tantalum polymer capacitors?
Higher cost: They are more expensive to produce than traditional aluminum electrolytic capacitors.
Lower withstand voltage: They are usually rated for lower working voltage than aluminum electrolytic capacitors of the same size.
Temperature sensitivity: They may not perform well in extreme temperatures, especially low temperatures.
Risk of physical damage: They may be damaged if subjected to mechanical stress or excessive current surges. -
2. How do you know that a capacitor is tantalum polymer?
Appearance markings: Usually the word "Polymer" is marked, along with the capacitance value, operating voltage, and positive and negative pole identification.
Packaging information: Check the
Technical specifications or data sheet on the product packaging. -
3. Which side of a tantalum polymer capacitor is the positive pole?
Usually, there is a clear mark on the tantalum polymer capacitor to indicate the positive pole, such as a long bar mark or a "+" symbol.
-
4. What causes tantalum polymer capacitors to fail?
Overvoltage operation: Exceeding the rated voltage may cause internal breakdown.
Reverse bias: Connecting the positive and negative terminals in reverse may cause immediate damage.
Overheating: Prolonged exposure to high temperature environments can affect performance and even cause failure.
Mechanical damage: Damage may also be caused by external impact or pressure.

