TPSA224K050R7000 vs T491C106K025AT7280
| Part Number |
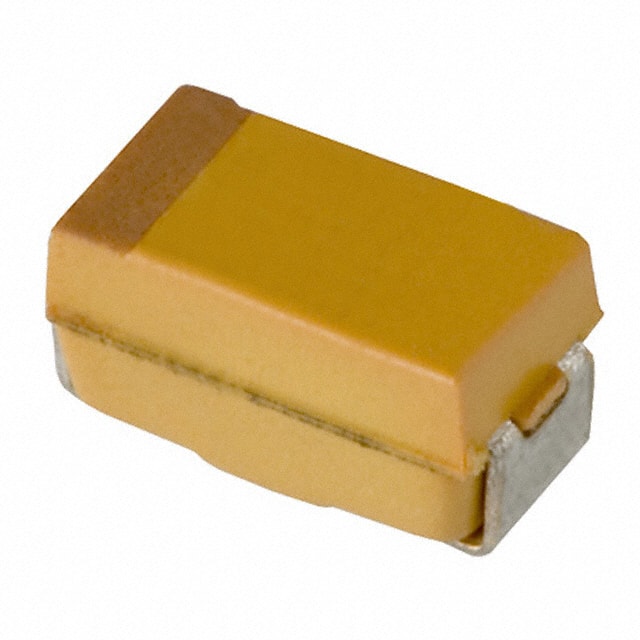

|
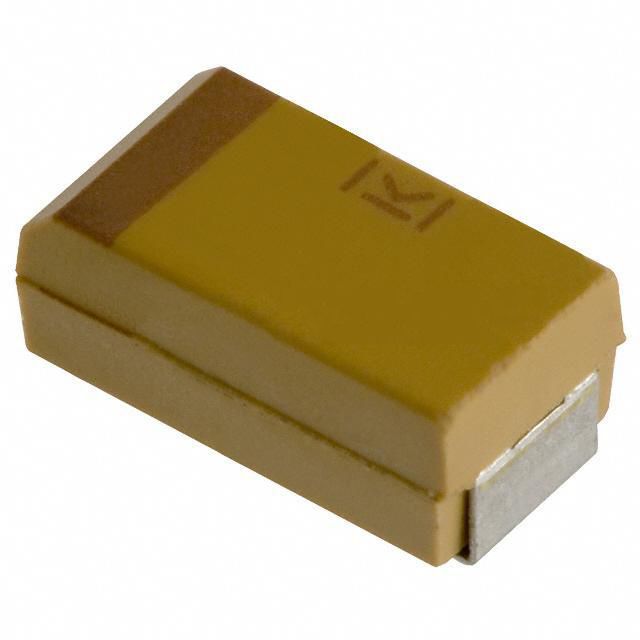

|
| Category | Tantalum Capacitors | Tantalum Capacitors |
| Manufacturer | KYOCERA AVX | KEMET |
| Description | CAP TANT 0.22UF 10% 50V 1206 | CAP TANT 10UF 10% 25V 2312 |
| Package | Tape & Reel (TR) | Cut Tape (CT) |
| Series | TPS | T491 |
| Type | Molded | Molded |
| Features | General Purpose | General Purpose |
| Operating Temperature | -55°C ~ 125°C | -55°C ~ 125°C |
| Mounting Type | Surface Mount | Surface Mount |
| Package / Case | 1206 (3216 Metric) | 2312 (6032 Metric) |
| Tolerance | ±10% | ±10% |
| Size / Dimension | 0.126" L x 0.063" W (3.20mm x 1.60mm) | 0.236" L x 0.126" W (6.00mm x 3.20mm) |
| Voltage - Rated | 50 V | 25 V |
| Lead Spacing | - | - |
| Ratings | - | - |
| Height - Seated (Max) | 0.071\" (1.80mm) | 0.110\" (2.80mm) |
| Capacitance | 0.22 µF | 10 µF |
| ESR (Equivalent Series Resistance) | 7Ohm | 1.5Ohm |
| Lifetime @ Temp. | - | 2000 Hrs @ 125°C |
| Failure Rate | - | - |
| Manufacturer Size Code | A | C |
-
1. Why are tantalum capacitors so expensive?
Tantalum ore resources are scarce and the mining cost is high.
The manufacturing process is complex and the yield is relatively low.
It has excellent electrical characteristics, making it indispensable in high-end applications. -
2. What is the expected life of tantalum capacitors?
Under normal circumstances, it can range from thousands of hours to tens of thousands of hours, depending on the working conditions and manufacturer specifications.
-
3. Can I use ceramic capacitors instead of tantalum capacitors?
It depends on the specific situation. If the size, ESR requirements are not high and a specific capacitance value is not required, you can consider replacing it.
But be aware that there are differences in physical properties between the two, and direct replacement may affect the working state of the circuit. -
4. What special precautions must be taken when installing tantalum capacitors?
Ensure the correct polarity connection.
Be careful not to exceed the rated voltage.
Use appropriate fuses or other protective devices to prevent overcurrent.
Consider heat dissipation design to avoid local overheating.

