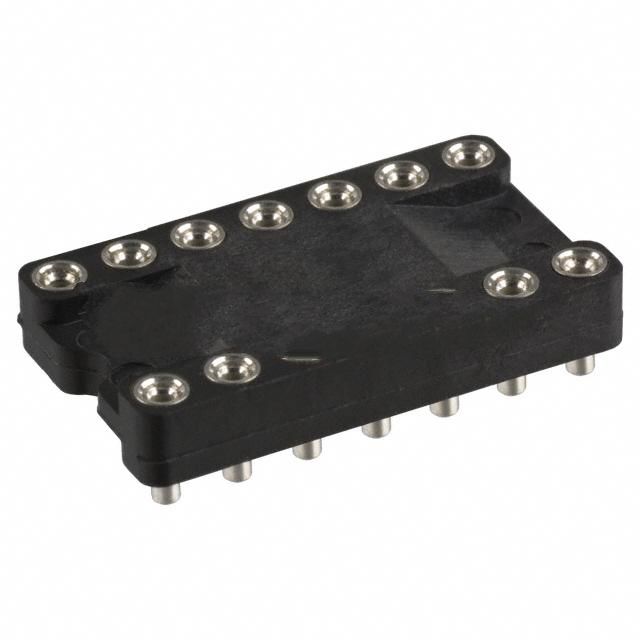
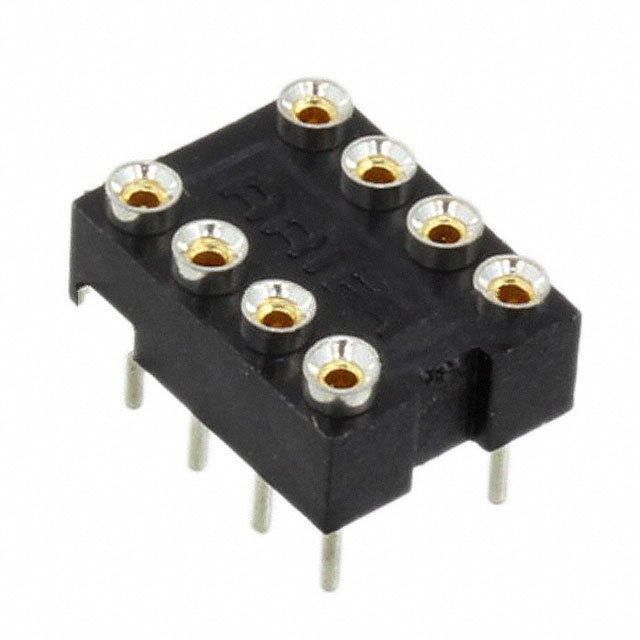
8452-11B1-RK-TP Product Introduction:
3M Part Number 8452-11B1-RK-TP(Sockets for ICs, Transistors), developed and manufactured by 3M, distributed globally by Jinftry. We distribute various electronic components from world-renowned brands and provide one-stop services, making us a trusted global electronic component distributor.
8452-11B1-RK-TP is one of the part numbers distributed by Jinftry, and you can learn about its specifications/configurations, package/case, Datasheet, and other information here. Electronic components are affected by supply and demand, and prices fluctuate frequently. If you have a demand, please do not hesitate to send us an RFQ or email us immediately sales@jinftry.com Please inquire about the real-time unit price, Data Code, Lead time, payment terms, and any other information you would like to know. We will do our best to provide you with a quotation and reply as soon as possible.
Sockets for ICs, Transistors are electronic components specifically designed to accommodate and connect integrated circuits (ICs) or transistors. One common type is to associate ZIFs with specific socket types, while another common type is sockets in the form of Pin Grid Array (PGA) packaging, allowing ICs or transistors to be easily inserted and removed without damaging the pins. This type of socket typically includes metal contact pads, an insulated base, and a locking mechanism, designed to ensure good electrical contact, physical stability, and convenient replacement and maintenance processes. The characteristics of this type of socket typically include high reliability, support for hot swapping in certain types, wide compatibility, and the ability to save space in high-density packaging environments.
Application
Sockets for ICs, Transistors are widely used in the electronics industry, especially in situations where ICs need to be frequently replaced or upgraded. In the field of computer hardware, CPU sockets make processor upgrades simple and fast, without the need to replace the entire motherboard. In communication equipment, such sockets can quickly replace faulty ICs, effectively shorten maintenance cycles, and reduce costs. In testing and measuring equipment, sockets are commonly used for temporary installation of various ICs for functional verification and performance testing. In addition, in fields such as industrial automation, automotive electronics, aerospace, and defense systems that require high reliability and maintainability, this type of socket also plays a key role in ensuring the high availability and easy maintenance of critical circuits.
FAQ about Sockets for ICs, Transistors
-
1. What is an IC socket?
An IC socket, or integrated circuit socket, is an electronic component used to be installed on a circuit board. Its main function is to insert and fix an integrated circuit (IC) chip. An IC socket is set in multiple cavities through multiple electrical contacts, so that the IC chip can be directly plugged in and out without the need to use a soldering iron for desoldering, thereby improving the flexibility of chip assembly and the convenience of repair and replacement.
Specifications and types of IC sockets
The specifications of IC sockets are diverse, and the common ones are 8, 16, 18, 20 pins and other specifications. In addition, the hole pitch of the IC socket is 2.54mm and 1.778mm, the shape is a round hole, and the arrangement is single row and double row. The number of pins ranges from 1 to 50P, and the exposed length of the PIN pin also has a variety of options, such as 7.43mm, 10.0mm, 12.2mm, 13.4mm and 17.8mm.
-
2. What is the main function of transistors?
A transistor is an electronic device whose main function is to amplify and control current: the transistor is an important milestone in the development of electronic technology and is widely used in various electronic devices and circuits.
The basic function of a transistor is to amplify current. The three regions in a transistor are the collector, emitter and base. The voltage change between the base and the emitter can control the current between the collector and the emitter, thereby amplifying the current. When the current between the base and the emitter is small, the current between the collector and the emitter increases many times, which is the amplification effect of the transistor.
Transistors can also be used as electronic switches. When the current between the base and the emitter is small, the current between the collector and the emitter is basically zero, and the transistor is in the off state. When the current between the base and the emitter increases to a certain extent, the current between the collector and the emitter increases sharply, and the transistor is in the on state. This switching characteristic can be widely used in digital circuits to realize the function of logic gates.
-
3. What are PNP and NPN transistors?
PNP and NPN transistors are two basic types of transistors, which have significant differences in structure and current flow direction.
Definition and structure
NPN transistor: It is composed of two N-type semiconductor regions sandwiching a P-type semiconductor region, forming three main regions of emitter (E), base (B) and collector (C). This structure makes the NPN transistor behave in the circuit similar to two PN junction diodes connected back to back.
PNP transistor: It is composed of an N-type semiconductor material doped between two P-type semiconductor materials, and also has three regions of emitter, base and collector, but the current flow direction and carrier type are opposite to those of NPN.
Working Principle
NPN transistor: When a forward bias voltage is applied between the emitter and the base, the free electrons in the emitter can cross the PN junction into the base and recombine with the holes in the base to generate a base current. A reverse bias voltage is applied between the collector and the base to prevent further flow of current. When a small input signal is applied to the base, this signal changes the voltage between the base and the emitter, thereby affecting the injection of free electrons in the emitter and forming a collector current. Since the collector current is an amplification of the base current, the NPN transistor has an amplification effect.
PNP transistor: The working principle is similar to that of the NPN type, but the current flow direction and carrier type are opposite. Positive charge flows from the emitter of the P-type semiconductor to the base, a part of which is captured by the base electrons of the N-type semiconductor and becomes the base current, and most of the rest becomes the collector current.
 Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Lead free / RoHS Compliant