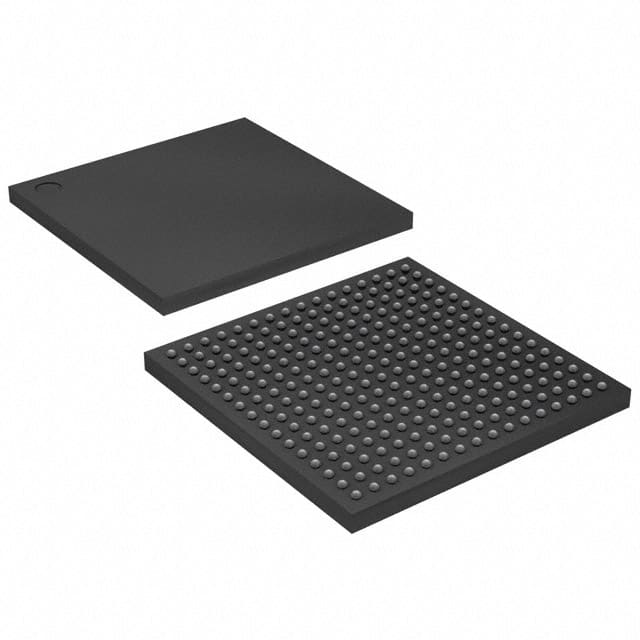
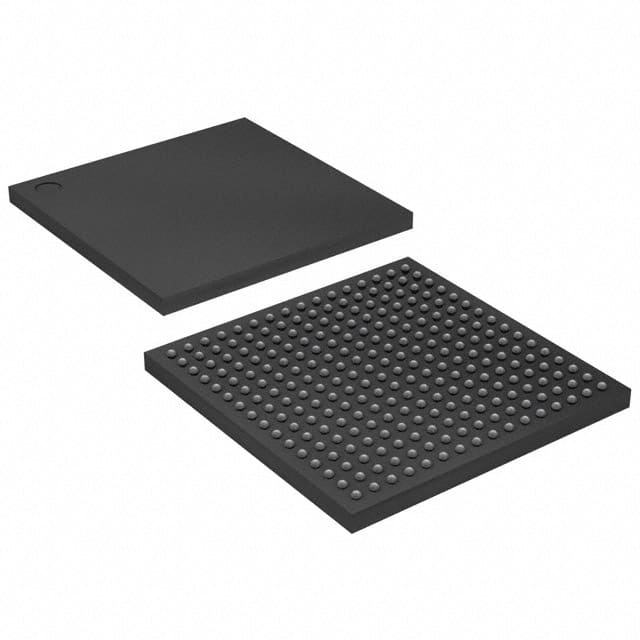
Intel EP3C10F256C6N
- EP3C10F256C6N
- Intel
- IC FPGA 182 I/O 256FBGA
- Embedded - FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Array)
- EP3C10F256C6N Datasheet
- 256-LBGA
- 256-LBGA
-
 Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Lead free / RoHS Compliant - 27950
- Spot Inventory / Athorized Dstributor / Factory Excess Stock
- 1 year quality assurance 》
- Click to get rates
What is EP3C10F256C6N
Intel Part Number EP3C10F256C6N(Embedded - FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Array)), developed and manufactured by Intel, distributed globally by Jinftry. We distribute various electronic components from world-renowned brands and provide one-stop services, making us a trusted global electronic component distributor.
EP3C10F256C6N is one of the part numbers distributed by Jinftry, and you can learn about its specifications/configurations, package/case, Datasheet, and other information here. Electronic components are affected by supply and demand, and prices fluctuate frequently. If you have a demand, please do not hesitate to send us an RFQ or email us immediately [email protected] Please inquire about the real-time unit price, Data Code, Lead time, payment terms, and any other information you would like to know. We will do our best to provide you with a quotation and reply as soon as possible.
EP3C10F256C6N Specifications
- Part NumberEP3C10F256C6N
- CategoryEmbedded - FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Array)
- ManufacturerIntel
- DescriptionIC FPGA 182 I/O 256FBGA
- Package256-LBGA
- SeriesCyclone® III
- Voltage - Supply1.15 V ~ 1.25 V
- Operating Temperature0°C ~ 85°C (TJ)
- Mounting TypeSurface Mount
- Package / Case256-LBGA
- Supplier Device Package256-FBGA (17x17)
- Number of I/O182
- Number of LABs/CLBs645
- Number of Logic Elements/Cells10320
- Total RAM Bits423936
Application of EP3C10F256C6N
EP3C10F256C6N Datasheet
EP3C10F256C6N Datasheet , 256-LBGA,Cyclone® III,1.15 V ~ 1.25 V,0°C ~ 85°C (TJ),Surface Mount,256-LBGA,256-FBGA (17x17),182,645,10320,423936
EP3C10F256C6N Classification
Embedded - FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Array)
FAQ about Embedded - FPGAs (Field Programmable Gate Array)
-
1. What is the hardware of FPGA?
FPGA (Field-Programmable Gate Array) is a hardware device, not software. FPGA is a programmable hardware device consisting of a large number of logic units, storage units and interconnection resources, which can realize complex digital circuits and system designs.
The hardware structure of FPGA mainly includes the following parts:
Logic unit: FPGA contains programmable logic blocks that can perform logical and arithmetic operations.
Interconnection resources: These resources act as connections between logic blocks, allowing data to be transferred between different logic blocks.
Memory unit: Used to store configuration information and temporary data, supporting FPGA operations and logic processing.
The characteristics and application scenarios of FPGA include:
Programmability: FPGA can change the structure of its internal circuits by loading configuration information to achieve different functions.
High-speed execution: FPGA performs logic operations at the hardware level, which is usually several orders of magnitude faster than software execution.
Wide application: FPGA is widely used in many fields such as communications, medical, automotive, aerospace, industrial automation, etc. to implement complex digital circuits and algorithms, improve equipment performance, reduce power consumption or achieve specific functional requirements. -
2. Can FPGAs replace microcontrollers?
FPGAs cannot completely replace microcontrollers (MCUs). Although FPGAs and MCUs have their own characteristics and advantages in functions and applications, FPGAs cannot completely replace MCUs. There are significant differences between FPGAs and MCUs in terms of programmability, processing power, flexibility, development cycle, and cost.
The main differences between FPGAs and MCUs include:
Programmability: FPGAs are programmable and can be reprogrammed to achieve new functions, while MCUs are fixed and cannot be changed.
Processing power: FPGAs are usually used in high-performance computing, digital signal processing, image processing, and other fields, while MCUs are usually used for simple tasks such as controlling and monitoring equipment and sensors.
Flexibility: FPGA is more flexible than MCU and can be programmed and reprogrammed according to different applications, while MCU can usually only run predefined programs in its internal memory.
Development cycle: FPGA has a longer development cycle than MCU because FPGA needs to be designed, verified and debugged, while MCU usually only needs to write and debug programs.
Cost: FPGA costs more than MCU because FPGA needs to be manufactured and tested, and a lot of design and verification work is required, while MCU has a relatively low cost.
In specific application scenarios, FPGA and MCU each have their own advantages:
Advantages of FPGA: high programmability, parallel processing capability, high performance, suitable for applications that require rapid prototyping and system upgrades, suitable for scenarios with high real-time requirements.
Advantages of MCU: high integration, low cost, low power consumption, suitable for scenarios with strict power consumption requirements.
In summary, although FPGA performs well in some high-performance and flexible application scenarios, MCU still has irreplaceable advantages in simple control and monitoring tasks. -
3. Is FPGA faster than CPU?
FPGAs are faster than CPUs in some cases. FPGAs are programmable hardware devices whose internal architecture can be configured by users as needed, which enables them to process multiple computing tasks in parallel, resulting in higher computing performance in some scenarios.
FPGAs and CPUs have different architectures and design goals. CPUs are general-purpose processors that can perform a variety of tasks, but may require multiple clock cycles to process specific operations. FPGAs, on the other hand, achieve specific computing structures by reorganizing circuits, and have higher parallelism and efficiency. For example, when processing specific tasks such as signals and images, FPGAs can complete them faster than CPUs.
The main advantage of FPGAs is their programmability and flexibility. FPGAs can be reprogrammed and reconfigured as needed, which enables designers to quickly test new and updated algorithms without developing and releasing new hardware, thereby speeding up time to market and saving costs. In addition, FPGAs offer the advantages of superior performance and reduced latency, and are suitable for real-time applications that require low latency and deterministic latency.
We are a professional PCB manufacturer who offers comprehensive PCB manufacturing services including: professional Ceramic PCB HDI PCB Heavy Copper PCB High-TG PCB High Speed PCB High Frequency PCB Metal Core PCB PCB fabrication and PCB assembly, providing fast turnaround prototypes for high-end products.
• Prompt Responsiveness
• Guaranteed Quality
• Global Access
• Competitive Market Price
• One-Stop support services of supply chain
Jinftry, Your most trustworthy component supplier, welcome to send us the inquiry, thank you!
Do you have any questions about EP3C10F256C6N ?
Feel free to contact us: