What is a Junction Diode? What are the types of junction diodes?

What is a Junction Diode? A junction diode is a semiconductor device consisting of a structure composed of a P-type semiconductor and an N-type semiconductor. It is also known as a PN junction diode or simply a diode. Junction diodes are one of the most basic and common types of diodes. You can also get a more detailed introduction to PN junction diodes from Wikipedia.
1. What are the types of junction diodes?
There are many different types of junction diodes, the most common of which are general-purpose diodes. In addition, there are some special types of junction diodes, including:
1) Fast Recovery Diode: It has a short recovery time and can be used in high-frequency circuits and switching power supplies.
2) Schottky Diode: With low forward voltage drop and fast switching characteristics, it is suitable for applications such as high-speed switches and mixers.
3) Zener Diode: It works in the reverse breakdown region and can be used as a voltage regulator and voltage reference source.
4) Photodiode: It can convert optical signals into electrical signals, and is often used in fields such as photoelectric detection and communication.
5) Variable capacitance diode: It has the characteristics of variable capacitance and is often used in radio frequency tuning and oscillation circuits.
2. What are the representative models of common junction diodes?
1N4148: This is a commonly used general-purpose fast recovery junction diode with a short recovery time and high switching speed. Click to learn more about the 1N4148 diode and its alternative models.

1N4007: This is a general-purpose rectifier diode with higher voltage and current capability, often used in power supply and rectification circuits, click to learn more about 1N4007 diode and its alternative models.
1N5819: This is a Schottky diode with low forward voltage drop and fast switching characteristics, suitable for high-frequency circuits and switching power supplies.
1N4733A: This is a Zener diode with a specific reverse breakdown voltage and is commonly used in voltage regulators and reference voltage sources.
1N6263: This is a fast recovery diode with a short recovery time and high switching speed, suitable for high-frequency circuits and switching power supplies.
3. What are the characteristics of junction diodes?
The structure of a junction diode consists of two differently-doped semiconductor materials. Impurity atoms in P-type semiconductors have excess holes (positive charge), while those in N-type semiconductors have excess electrons (negative charge). When P-type and N-type semiconductors are connected together in a specific way, a PN junction is formed.
1) Forward conduction characteristics: When a forward voltage is applied to the PN junction, also known as forward bias, the holes in the P region and the electrons in the N region will be pushed to the depletion region, causing the PN junction to become conductive, forming a state of forward current flow, which is called forward conduction. In the forward conducting state, junction diodes have low resistance.
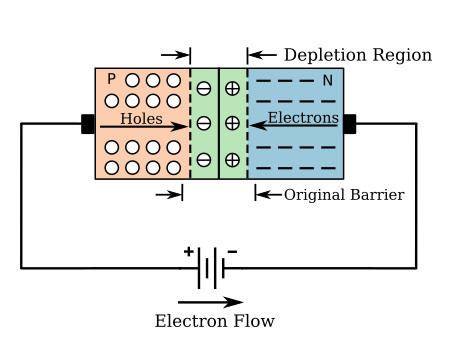
Image source: ecstudiosystems
2) Reverse cut-off characteristics: When a reverse voltage is applied on the PN junction, also known as reverse bias, the holes in the P region and the electrons in the N region will be attracted away from the depletion region, increasing the width of the depletion region. This makes the PN junction non-conductive and almost no current flows through it, which is called reverse blocking.
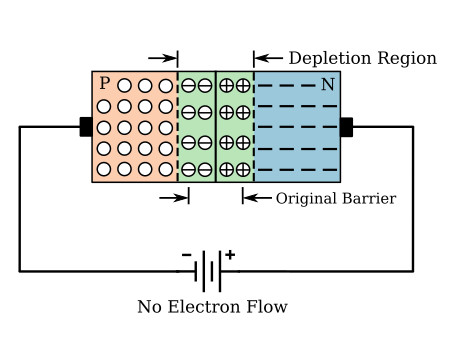
Image source: ecstudiosystems
3) Forward voltage drop: When the junction diode is in the forward conduction state, there will be a forward voltage drop, generally 0.6V to 0.7V. This forward voltage drop results in a voltage difference between the voltage source and the junction diode.
4) Reverse breakdown: When the reverse voltage exceeds the breakdown voltage of the junction diode, the junction diode will enter a reverse breakdown state, allowing current to pass. Reverse breakdown can be controllable (like a Zener diode) or irreversible.
4. What are the applications of junction diodes?
1) Rectifier: Junction diodes can be used as rectifiers to convert alternating current to direct current. Ordinary diodes allow current to pass in their forward conducting state and block current flow in their reverse blocking state. This characteristic makes them ideal for use as rectifiers in power supplies and circuits.
2) Protection device: Junction diodes can be used as protection devices for circuits to prevent damage from overvoltage and current. For example, fast recovery diodes are used in switching power supplies and inductive devices to quickly return to normal operating conditions, thereby providing circuit protection.
3) Signal Conditioning: Junction diodes can be used in signal conditioning and processing circuits. For example, Schottky diodes have low forward voltage drop and fast switching characteristics, so they are often used in high-frequency circuits, mixers, and switching circuits.
4) Electrostatic discharge protection: Junction diodes can be used in electrostatic discharge protection circuits. Electrostatic discharge can damage electronic equipment, and Zener diodes can provide a lower breakdown voltage as an electrostatic protection device to absorb and discharge electrostatic discharge.
5) Temperature measurement: The junction diode (such as temperature compensation diode) in the temperature sensor can change the current or voltage according to the change of temperature, so as to realize temperature measurement and control.
6) Light detection: Photodiodes can be used in photoelectric detection and communication applications. When light shines on a photodiode, it generates a current that can be used to measure the intensity of the light and the frequency of the light.
7) Voltage Reference: Zener diodes can be used as voltage regulators and voltage reference sources. Under a stable reverse breakdown voltage, the Zener diode can provide a relatively stable reference voltage.
Jinftry needs to emphasize that although PN junction diodes are made of semiconductor materials such as silicon, germanium, and gallium arsenide, silicon is preferable to germanium for designing diodes. Compared with pn junction diodes made of germanium semiconductors, PN junction diodes made of silicon semiconductors operate at higher temperatures. It should be noted that although junction diodes are an important basic component in many applications, their applications go far beyond the few areas listed above. The widespread use of junction diodes in electronics has made them an integral part of modern electronic devices and circuits.






