What is an LED light-emitting diode and how it works?
In various fields of modern technology and life, we often hear the word "LED". Whether it is lighting, display, or communication, LED has become an irreplaceable technology. So, what is an LED light-emitting diode, and how does it work? Jinftry solves this mystery of technology full of mystery for you.
1. What is an LED light-emitting diode?
LED, Full name Light Emitting Diode, is an electronic device that can convert electrical energy into light energy. Unlike ordinary light bulbs or fluorescent lamps, LED is a solid-state light source with the advantages of small size, energy saving, long life, and bright colors. Due to these characteristics, LEDs are widely used in various fields, from daily lighting to high-definition display to optical communication.
2. The working principle of LED: the shining light of the semiconductor
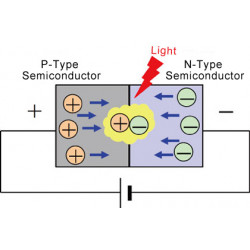
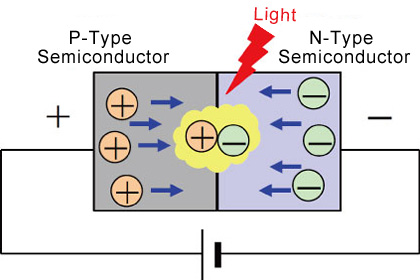
Understanding how LEDs work requires some basic knowledge of semiconductor physics. Semiconductor materials, such as silicon, gallium, gallium arsenide, etc., have conduction characteristics between conductors and insulators. When a dopant is introduced into a semiconductor material to form two regions, P-type (positive type) and N-type (negative type), a P-N junction is formed.
When an appropriate voltage is applied to the P-N junction, electrons flow from the N region to the P region, while holes flow from the P region to the N region. Near the P-N junction, electrons and holes recombine to release energy. According to the law of conservation of energy, this energy will be released in the form of photons, resulting in visible light. This is how LEDs emit light, known as radiative recombination.
Different semiconductor materials and dopants can produce different energy band structures, which determine the color of light emitted by LEDs. For example, LEDs made of gallium arsenide usually emit red light, and LEDs made of gallium nitride can emit light of different colors such as blue, green, and purple. This flexibility in material choice enables LEDs to cover a broad spectral range.
3. Application of LED: from lighting to innovation
The application range of LED is very wide, it has penetrated into every aspect of our daily life.
In the field of lighting, traditional incandescent and fluorescent lamps are gradually replaced by LED lighting. The energy efficiency and long life of LED make it a leader in the lighting industry. At the same time, the characteristics of dimmability and colorful lighting also enable LED lighting to create a variety of comfortable light environments.
In the field of display, LED technology has also been widely used. From smartphones and tablets to TVs, LED displays have become mainstream. By adjusting the color and brightness of the LED, we can obtain more realistic and clear images and videos.
In addition, LEDs also have unique applications in communication, agriculture, medicine, and other fields. Visible light communication (VLC) utilizes the fast switching characteristics of LEDs to achieve high-speed data transmission. In agriculture, precise regulation of LED light sources can promote plant growth. In the medical field, LEDs are used in applications such as phototherapy and imaging, bringing new possibilities for medical diagnosis and treatment.
4. Future outlook: keep innovating and continue to shine
With the continuous advancement of science and technology, LED technology is also constantly innovating. In the future, LEDs may achieve higher brightness and higher efficiency, further expanding their application fields. The development of quantum dot technology and OLED technology will further improve the quality of LED displays and lighting.
At the same time, LED also has excellent development potential in emerging fields such as wearable devices, virtual reality, and augmented reality. We may see LEDs bring us a more intelligent and convenient life experience in the near future.
5. What determines the color of the LED?
The color of an LED is determined by the materials used in the semiconductor components. The two main materials used in LEDs are aluminum gallium indium phosphide and indium gallium nitride. Aluminum alloys are used to obtain red, orange, and yellow light, and indium alloys are used to obtain green, blue, and white light. Slight changes in the composition of these alloys alter the color of the emitted light.
6. What are the LED types?
Below is a list of different types of LEDs designed using semiconductors:
1) Micro LED
2) High Power LEDs
3) Flash LED
4) Two-color and three-color
5) Red, green, and blue LEDs
6) Alphanumeric LEDs
7) Lighting LEDs
7、The relationship between LED light-emitting diodes and junction diodes
LED (Light Emitting Diode, LED) is a special type of diode, which has the characteristics of ordinary junction diodes (Rectifier Diode), and can also convert electrical energy into light energy, thereby emitting visible light. Therefore, it can be said that an LED is a junction diode with a light-emitting function. For an introduction to junction diodes, click to learn more.
In Conclusion
LED light-emitting diode, as a solid-state light source, has shown great potential and prospects in various fields due to its high efficiency, energy saving, long life, and other characteristics. By gaining a deeper understanding of how LEDs work, we can better understand this fantastic technology and appreciate its integral role in modern technology. On the road of science and technology, LED will continue to shine and bring us a brighter future.







