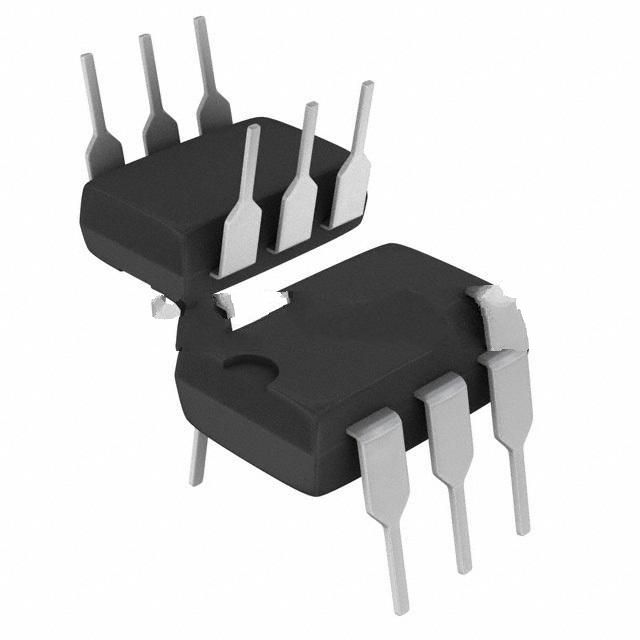
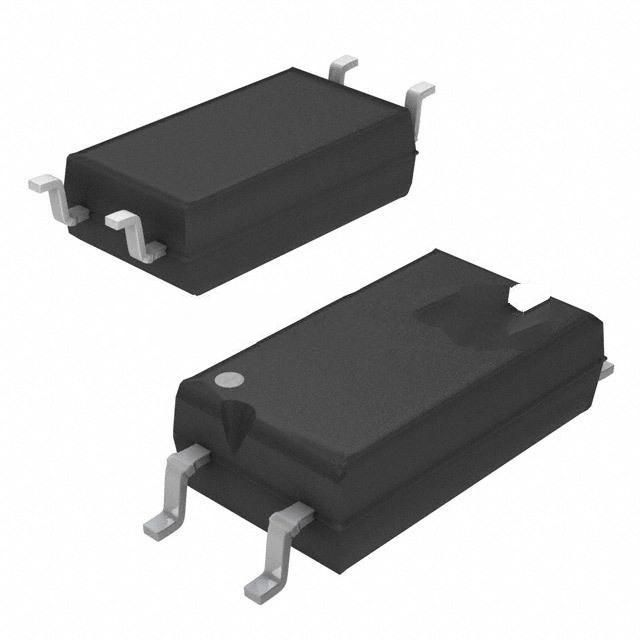
CNY17-3 vs TLP383(D4BLLTL,E
| Part Number |
|
|
| Category | Optoisolators - Transistor, Photovoltaic Output | Optoisolators - Transistor, Photovoltaic Output |
| Manufacturer | Vishay Semiconductor Opto Division | Toshiba Semiconductor and Storage |
| Description | OPTOISO 5KV TRANS W/BASE 6DIP | OPTOISO 5KV TRANSISTOR SO6L |
| Package | 6-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm) | 6-SOIC (0.173", 4.40mm Width) 4 Leads |
| Series | - | - |
| Operating Temperature | -55°C ~ 110°C | -55°C ~ 125°C |
| Mounting Type | Through Hole | Surface Mount |
| Package / Case | 6-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm) | 6-SOIC (0.173", 4.40mm Width), 4 Leads |
| Supplier Device Package | 6-DIP | 6-SO |
| Output Type | Transistor with Base | Transistor |
| Voltage - Output (Max) | 70V | 80V |
| Number of Channels | 1 | 1 |
| Input Type | DC | DC |
| Voltage - Isolation | 5000Vrms | 5000Vrms |
| Rise / Fall Time (Typ) | 2µs, 2µs | 2µs, 3µs |
| Voltage - Forward (Vf) (Typ) | 1.39V | 1.25V |
| Current - DC Forward (If) (Max) | 60mA | 50mA |
| Current - Output / Channel | 50mA | 50mA |
| Current Transfer Ratio (Min) | 100% @ 10mA | 200% @ 500µA |
| Current Transfer Ratio (Max) | 200% @ 10mA | 400% @ 500µA |
| Vce Saturation (Max) | 400mV | 300mV |
| Turn On / Turn Off Time (Typ) | 3µs, 2.3µs | 3µs, 3µs |
-
1. What is a transistor output optocoupler?
A transistor output optocoupler is a photocoupler, and its internal structure usually includes a light-emitting diode (LED) and a phototransistor. When the electrical signal at the input end drives the LED to emit light, the phototransistor generates a photocurrent after receiving the light signal, and then outputs it after amplification, thereby completing the "electricity -> light -> electricity" conversion and realizing the isolation between input and output.
-
2. What is a transistor output?
Transistor output is an output mode in circuit control, mainly used for controlling actuators (such as motors and electromagnets) in automation equipment. Transistor output realizes the switching control of the circuit through a semiconductor device, a transistor. As an electronic switch, the transistor has the characteristics of fast response and high-frequency action, and is suitable for application scenarios that require high-speed switching.
-
3. What is the role of the optical isolator?
The main function of the optical isolator is to allow light to pass in one direction and prevent light from passing in the opposite direction, thereby limiting the transmission direction of light and ensuring that light can only be transmitted in one direction. This characteristic makes the optical isolator play an important role in optical fiber communication systems, which can isolate reflected light and prevent the adverse effects of backward transmission light on the light source and optical path system.
-
4. What is the difference between an optocoupler and an optical isolator?
The main difference between an optocoupler and an optical isolator is their operating voltage range and application scenarios.
Optocouplers are suitable for circuits with a potential difference of less than 5000V, and are mainly used to maintain electrical isolation when transmitting data between two circuits. They are often used in circuits that operate at low voltages, such as microcontroller interfaces and solid-state relays. Optocouplers achieve electrical isolation by using a light emitting diode (LED) to convert an input electrical signal into an optical signal, which is then received and converted back into an electrical signal by a light detector such as a photodiode, phototransistor, or photodarlington.
Optical isolators are suitable for high voltage circuits with a potential difference of more than 5000V, and are mainly used to transmit analog or digital data between systems while maintaining isolation of power systems. They are commonly used in high voltage applications such as power systems, switching power supplies, and microcontrollers. Optical isolators are designed to isolate power systems with voltages ranging from 5000V to 50,000V or more, ensuring that the high voltage does not interfere with or damage the low voltage side.

