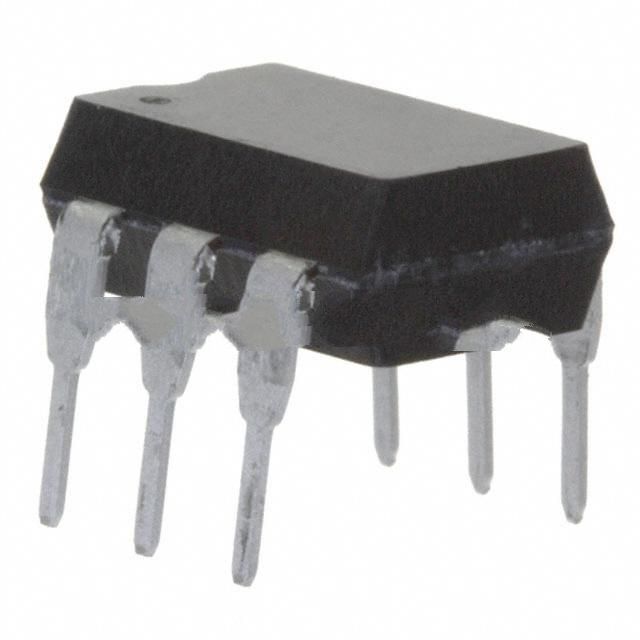
Vishay Semiconductor Opto Division CNY17-3
- CNY17-3
- Vishay Semiconductor Opto Division
- OPTOISO 5KV TRANS W/BASE 6DIP
- Optoisolators - Transistor, Photovoltaic Output
- CNY17-3 Datasheet
- 6-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
- 6-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
-
 Lead free / RoHS Compliant
Lead free / RoHS Compliant - 27829
- Spot Inventory / Athorized Dstributor / Factory Excess Stock
- 1 year quality assurance 》
- Click to get rates
What is CNY17-3
Vishay Semiconductor Opto Division Part Number CNY17-3(Optoisolators - Transistor, Photovoltaic Output), developed and manufactured by Vishay Semiconductor Opto Division, distributed globally by Jinftry. We distribute various electronic components from world-renowned brands and provide one-stop services, making us a trusted global electronic component distributor.
CNY17-3 is one of the part numbers distributed by Jinftry, and you can learn about its specifications/configurations, package/case, Datasheet, and other information here. Electronic components are affected by supply and demand, and prices fluctuate frequently. If you have a demand, please do not hesitate to send us an RFQ or email us immediately [email protected] Please inquire about the real-time unit price, Data Code, Lead time, payment terms, and any other information you would like to know. We will do our best to provide you with a quotation and reply as soon as possible.
CNY17-3 Specifications
- Part NumberCNY17-3
- CategoryOptoisolators - Transistor, Photovoltaic Output
- ManufacturerVishay Semiconductor Opto Division
- DescriptionOPTOISO 5KV TRANS W/BASE 6DIP
- Package6-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
- Series-
- Operating Temperature-55°C ~ 110°C
- Mounting TypeThrough Hole
- Package / Case6-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm)
- Supplier Device Package6-DIP
- Output TypeTransistor with Base
- Voltage - Output (Max)70V
- Number of Channels1
- Input TypeDC
- Voltage - Isolation5000Vrms
- Rise / Fall Time (Typ)2µs, 2µs
- Voltage - Forward (Vf) (Typ)1.39V
- Current - DC Forward (If) (Max)60mA
- Current - Output / Channel50mA
- Current Transfer Ratio (Min)100% @ 10mA
- Current Transfer Ratio (Max)200% @ 10mA
- Vce Saturation (Max)400mV
- Turn On / Turn Off Time (Typ)3µs, 2.3µs
Application of CNY17-3
CNY17-3 Datasheet
CNY17-3 Datasheet , 6-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm),-55°C ~ 110°C,Through Hole,6-DIP (0.300", 7.62mm),6-DIP,Transistor with Base,70V,1,DC,5000Vrms,2µs, 2µs,1.39V,60mA,50mA,100% @ 10mA,200% @ 10mA,400mV,3µs, 2.3µs
CNY17-3 Classification
Optoisolators - Transistor, Photovoltaic Output
FAQ about Optoisolators - Transistor, Photovoltaic Output
-
1. What is the difference between optocouplers and opto-isolators?
The main difference between optocouplers and opto-isolators is their operating voltage range and application scenarios.
Operating voltage range
Optocouplers: Applicable to circuits with a potential difference of less than 5000V, used to maintain electrical isolation when transmitting data between two circuits.
Opto-isolators: Applicable to high-voltage circuits with a potential difference of more than 5000V, used to transmit analog or digital data between systems, ensuring that the isolation voltage of the power system is 5000 to 50,000V or more.
Application scenarios
Optocouplers: Commonly used in low-voltage circuits, such as microcontroller interfaces, allowing microcontrollers to safely control high-power devices, providing high resistance and effective isolation.
Opto-isolators: Applicable to high-voltage applications, such as solid-state relays and optical encoders, ensuring isolation between sensitive measurement circuits and high-power control circuits. -
2. What is a transistor output?
Transistor output is an output mode in circuit control, mainly used for controlling actuators (such as motors and electromagnets) in automation equipment. Transistor output realizes the switching control of the circuit through a semiconductor device, a transistor. As an electronic switch, the transistor has the characteristics of fast response and high-frequency action, and is suitable for application scenarios that require high-speed switching.
-
3. What is the difference between an optocoupler and an optical isolator?
The main difference between an optocoupler and an optical isolator is their operating voltage range and application scenarios.
Optocouplers are suitable for circuits with a potential difference of less than 5000V, and are mainly used to maintain electrical isolation when transmitting data between two circuits. They are often used in circuits that operate at low voltages, such as microcontroller interfaces and solid-state relays. Optocouplers achieve electrical isolation by using a light emitting diode (LED) to convert an input electrical signal into an optical signal, which is then received and converted back into an electrical signal by a light detector such as a photodiode, phototransistor, or photodarlington.
Optical isolators are suitable for high voltage circuits with a potential difference of more than 5000V, and are mainly used to transmit analog or digital data between systems while maintaining isolation of power systems. They are commonly used in high voltage applications such as power systems, switching power supplies, and microcontrollers. Optical isolators are designed to isolate power systems with voltages ranging from 5000V to 50,000V or more, ensuring that the high voltage does not interfere with or damage the low voltage side.
We are a professional PCB manufacturer who offers comprehensive PCB manufacturing services including: professional Ceramic PCB HDI PCB Heavy Copper PCB High-TG PCB High Speed PCB High Frequency PCB Metal Core PCB PCB fabrication and PCB assembly, providing fast turnaround prototypes for high-end products.
• Prompt Responsiveness
• Guaranteed Quality
• Global Access
• Competitive Market Price
• One-Stop support services of supply chain
Jinftry, Your most trustworthy component supplier, welcome to send us the inquiry, thank you!
Do you have any questions about CNY17-3 ?
Feel free to contact us:
















.jpg)

.jpg)